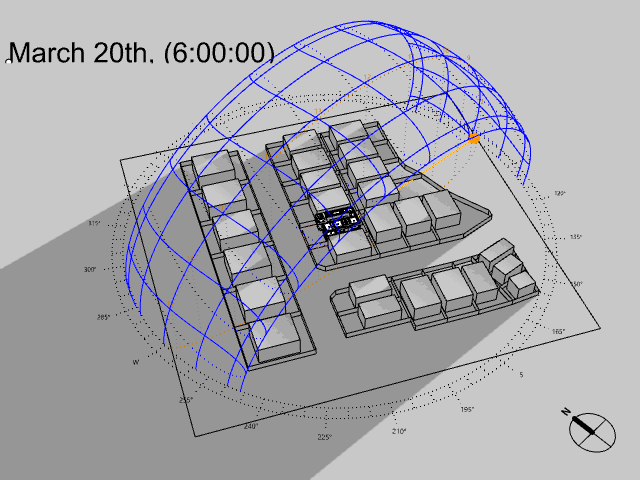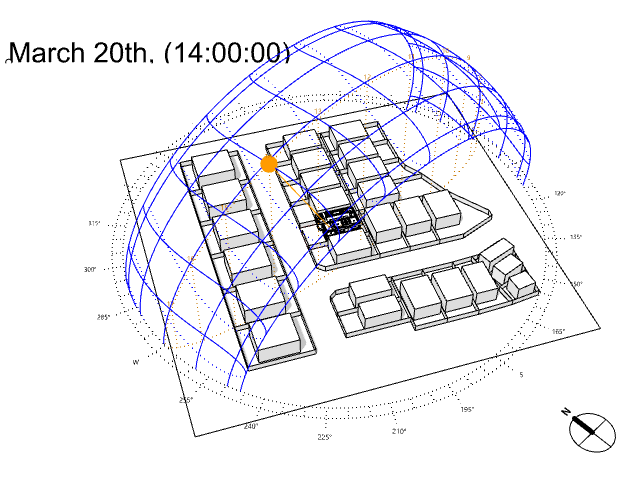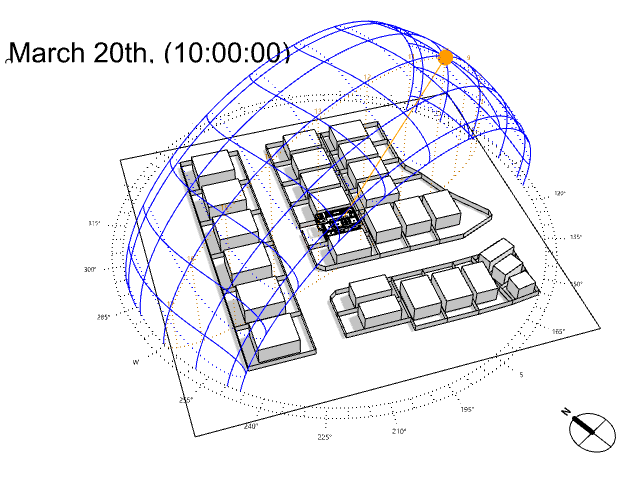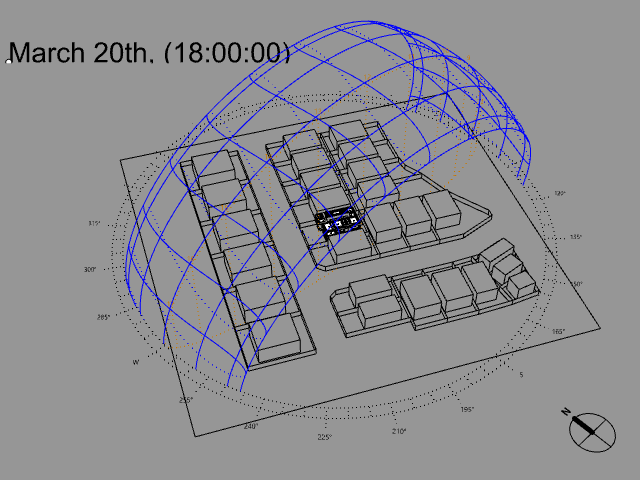
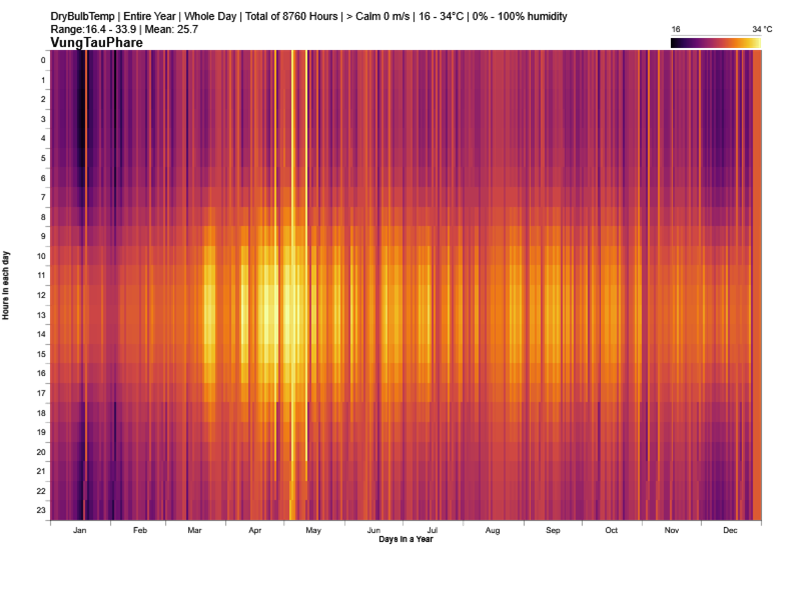
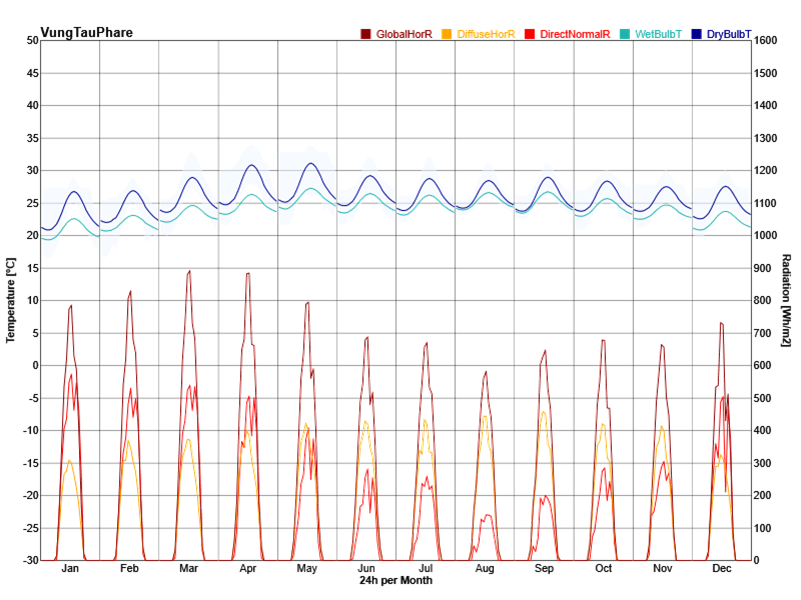
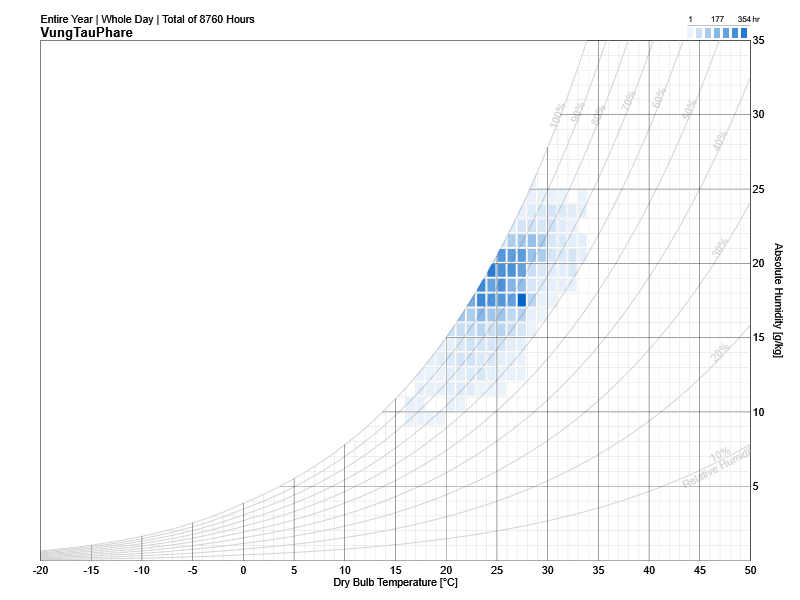
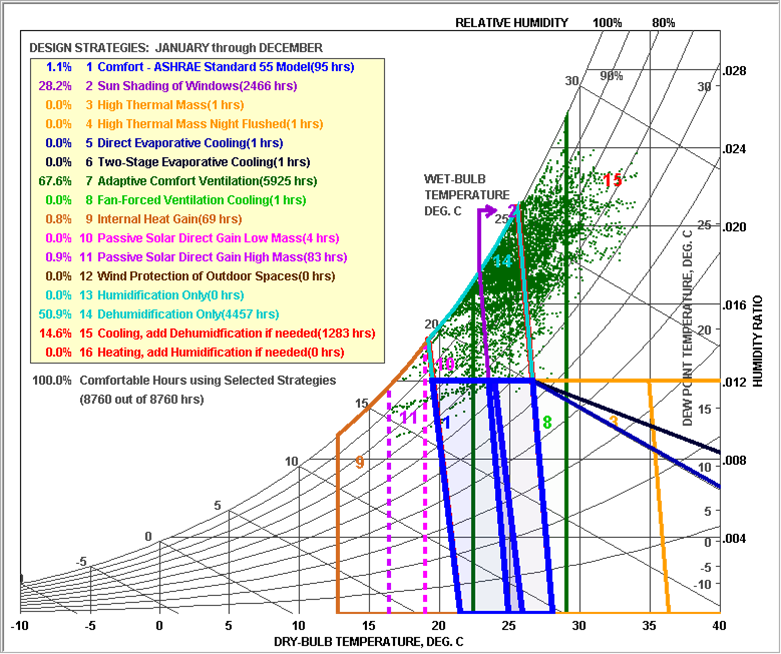
Several sorts of site and climate studies are supported by this work, including sun path and wind diagrams, shadow studies, psychrometric charts, and hourly/diurnal weather data plots.
Outdoor Thermal Comfort:
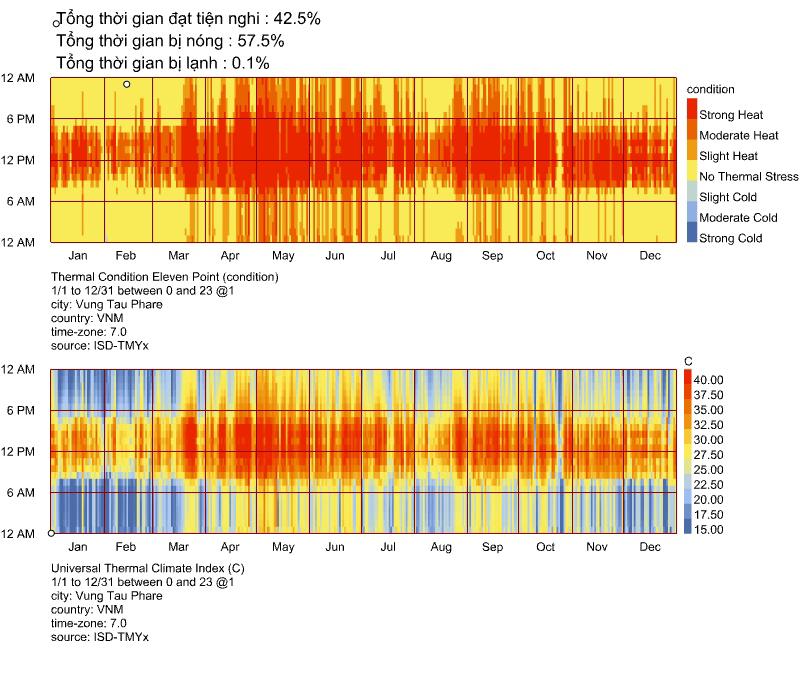
Based on the meteorological information, calculate the temperature and UTCI of the building site at each specified elevation.
UTCI(Universal Thermal Climate Index) is a bioclimatic index for describing the physiological comfort of the human body under specific meteorological conditions.
For example, imagine it is 0°C outside but on a very sunny day. The real temperature is 0°C, but you may easily feel it is like 12°C under the intense sun. On the contrary, imagine now that suddenly a big, dense and dark cloud covers the sun and some intense wind starts to blow. It is still 0°C but you may feel it’s now like -10°C.
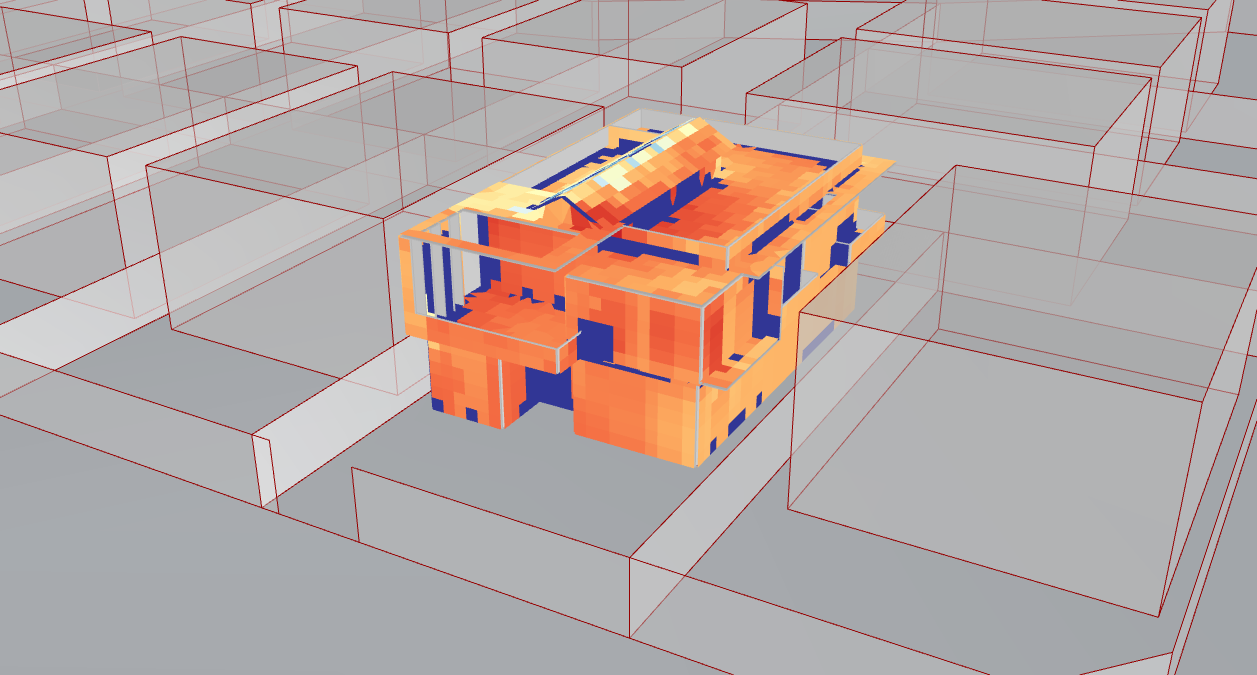
Outdoor Airflow :
The weather, as well as the nearby structures, will affect the building's wind impact. The simulation's visual representations will aid in visualizing the true wind direction and pressure acting on the structure.

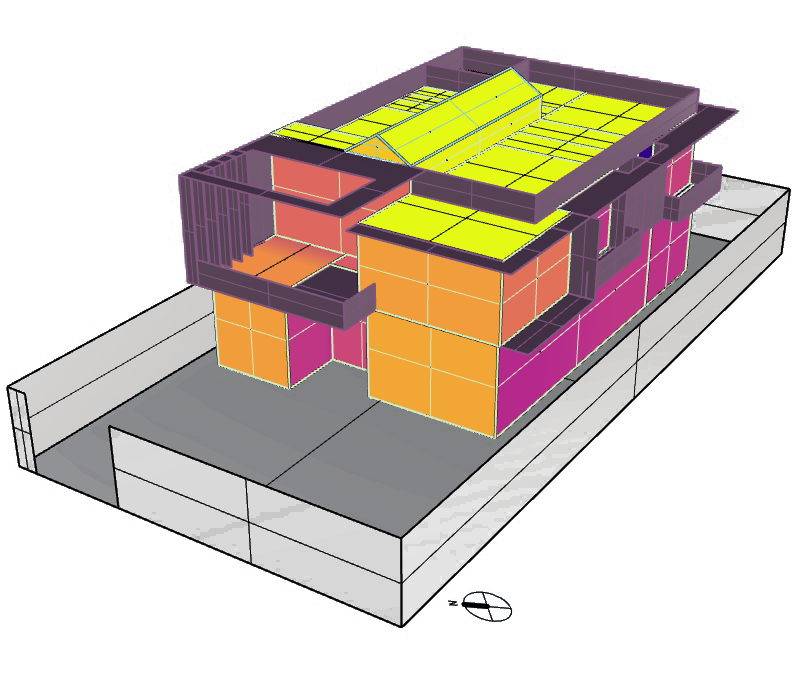
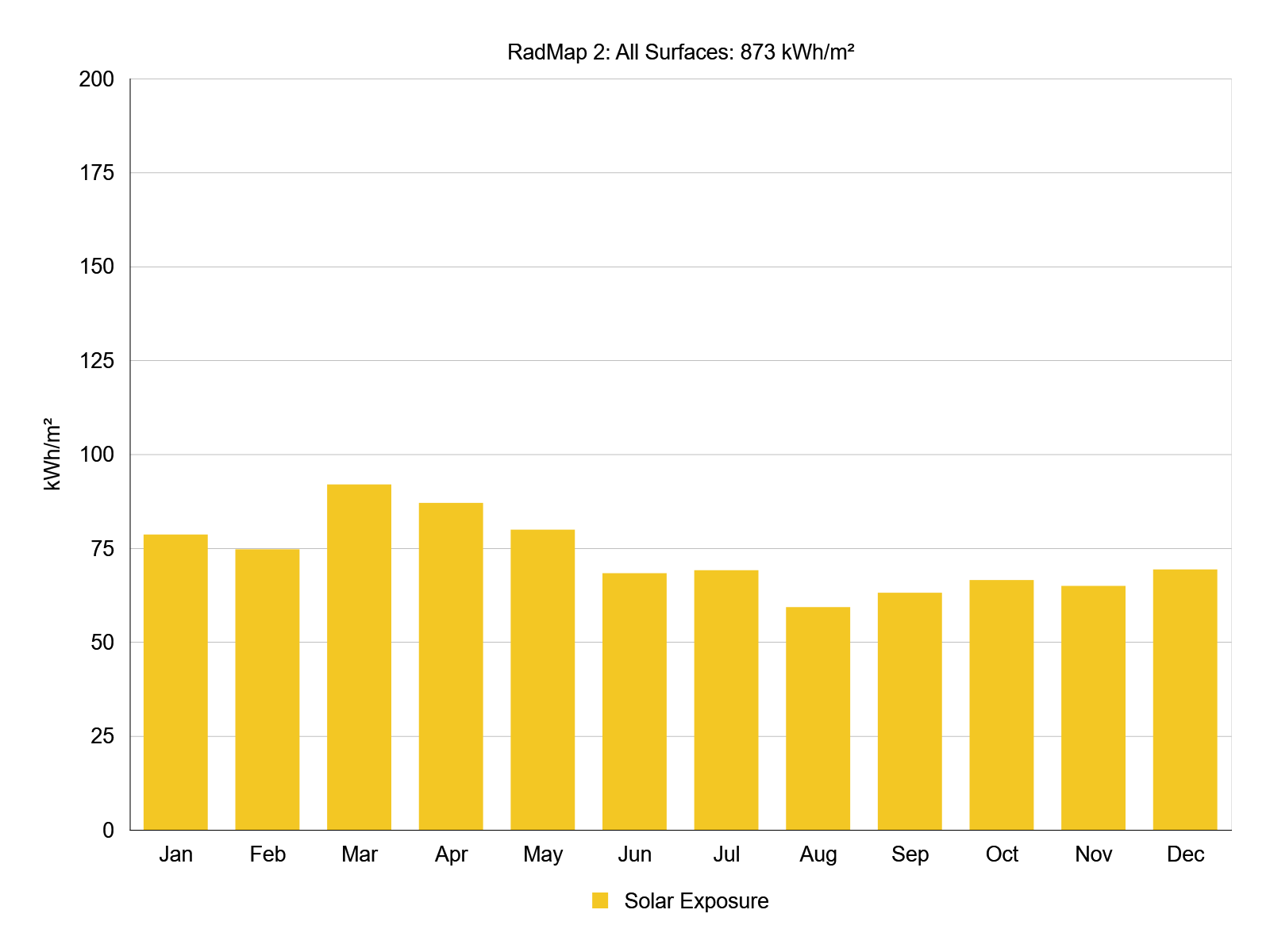
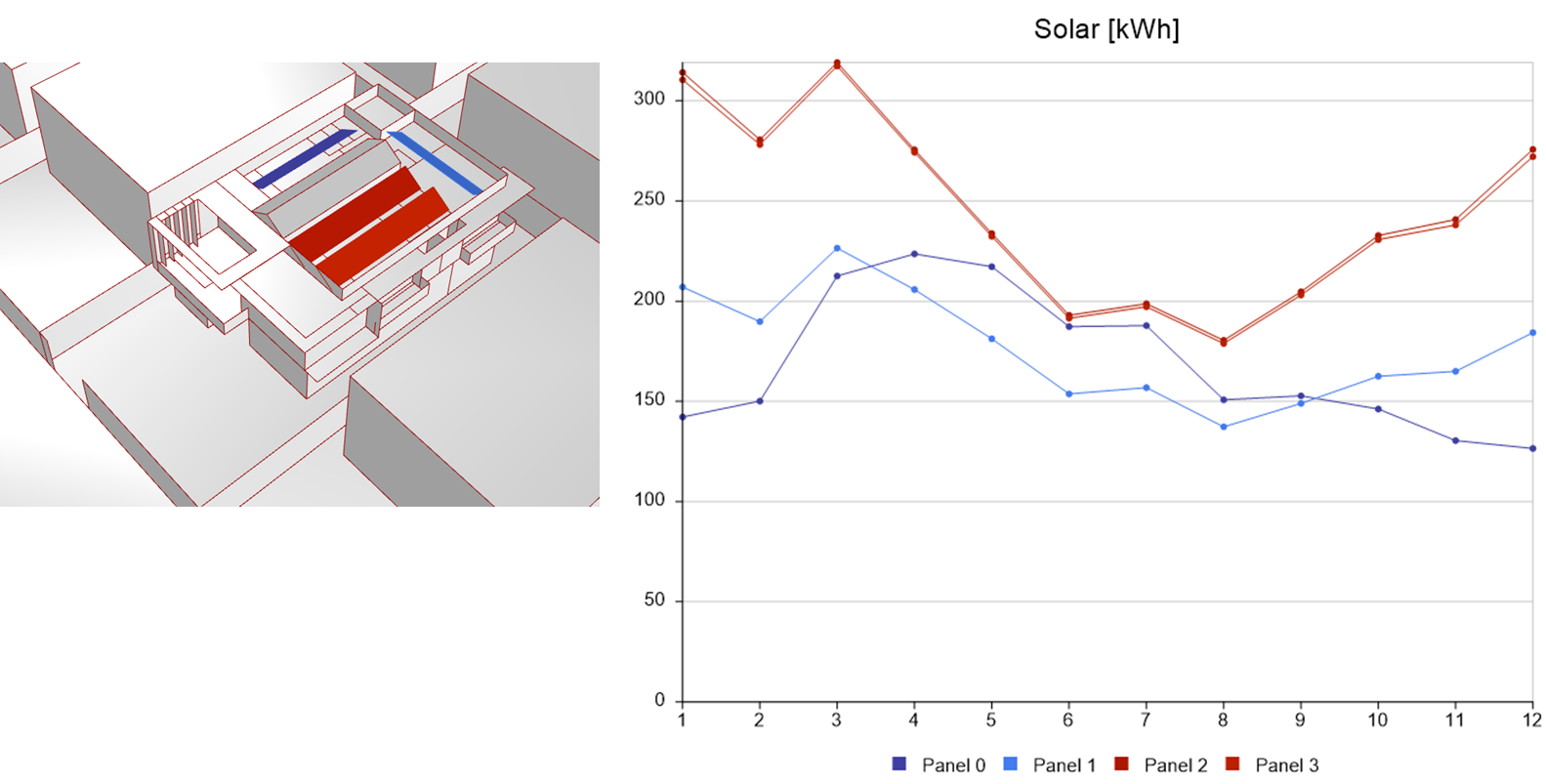
Radiation Map :
Calculation of the impact of solar radiation on the building's surface. Aids in the optimization of the building's shape and orientation, as well as the more effective placement of openings, doors, and shading objects. The efficiency of PV panels at various places is calculated.
Daylight :
This work supports the calculation of a variety of daylight availability metrics and is evaluated according to LEED, BREEAM, EN, etc…

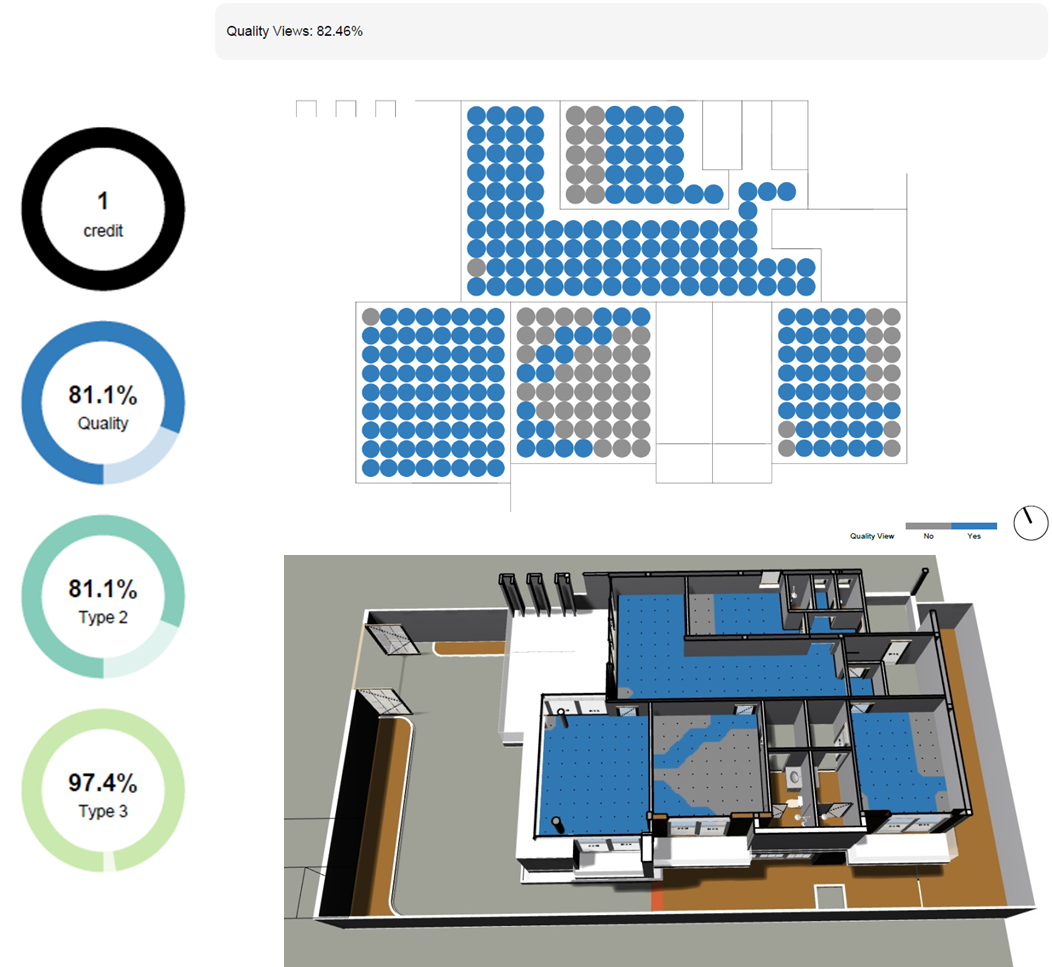
View Quality :
This work assesses occupant views and computes eligibility for the LEED v4 Quality Views credit (and the EN 17037 European standard).
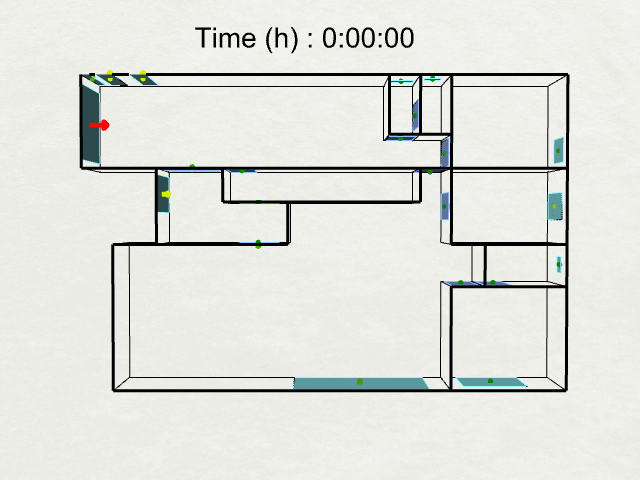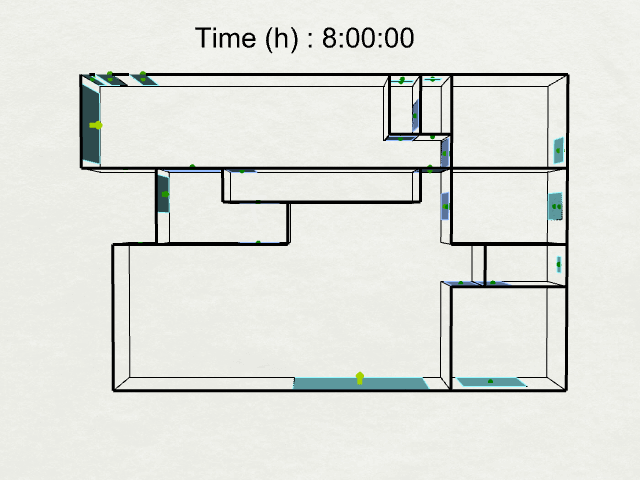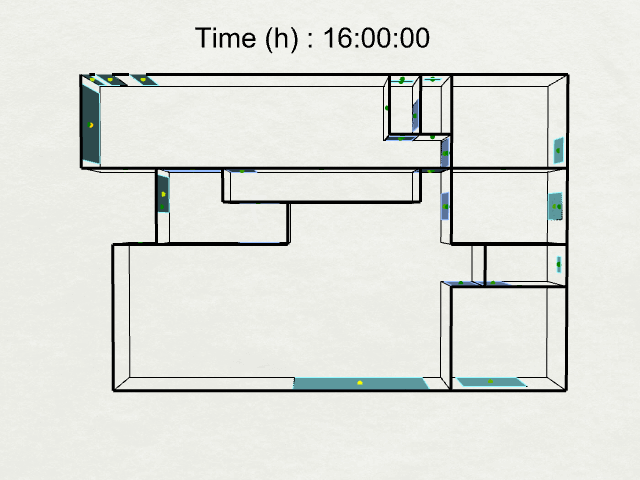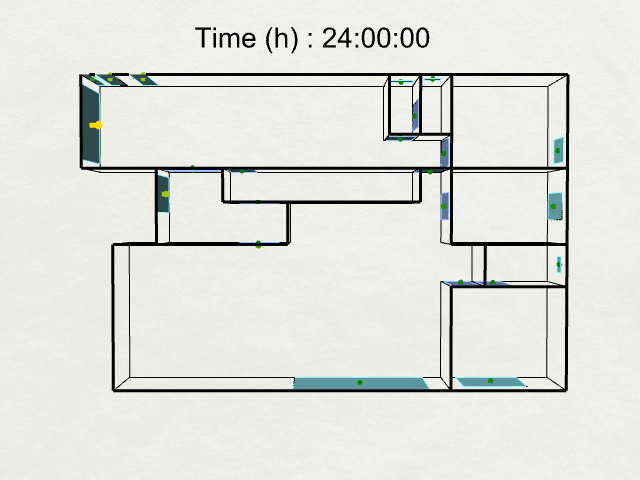
Thermal Analysis :
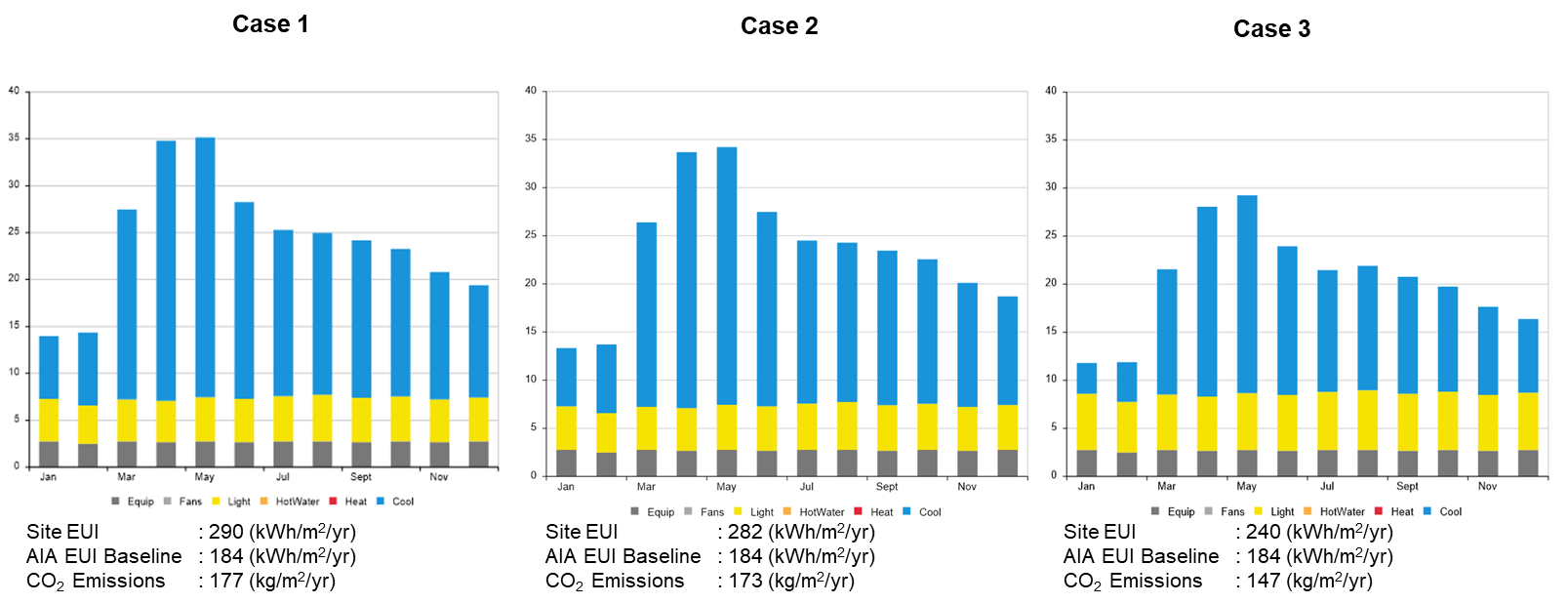
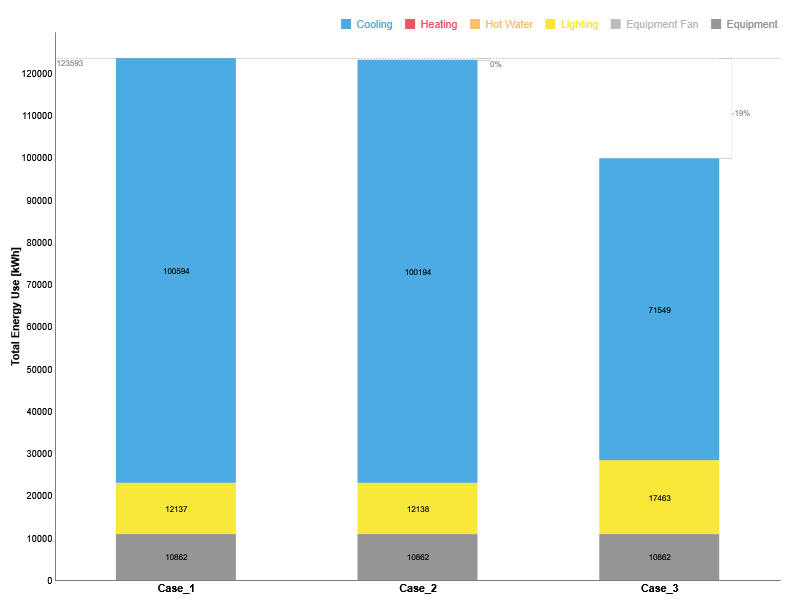
Airflow Network Model Uses the airflow network in EnergyPlus to calculate airflows in a naturally ventilated building. The outputs of the Energy Uses workflow will be computed for the entire building, including the site energy use intensity (EUI), annual carbon emissions, and operational energy costs.
Visibility :
This workflow shows how to quantify the visual connection to the outdoors as a percent of the full 360 fields of view; aids in determining the ability to see an object or landscape outside from within the house, as well as the ability to see what is inside the house from a specific outside location.
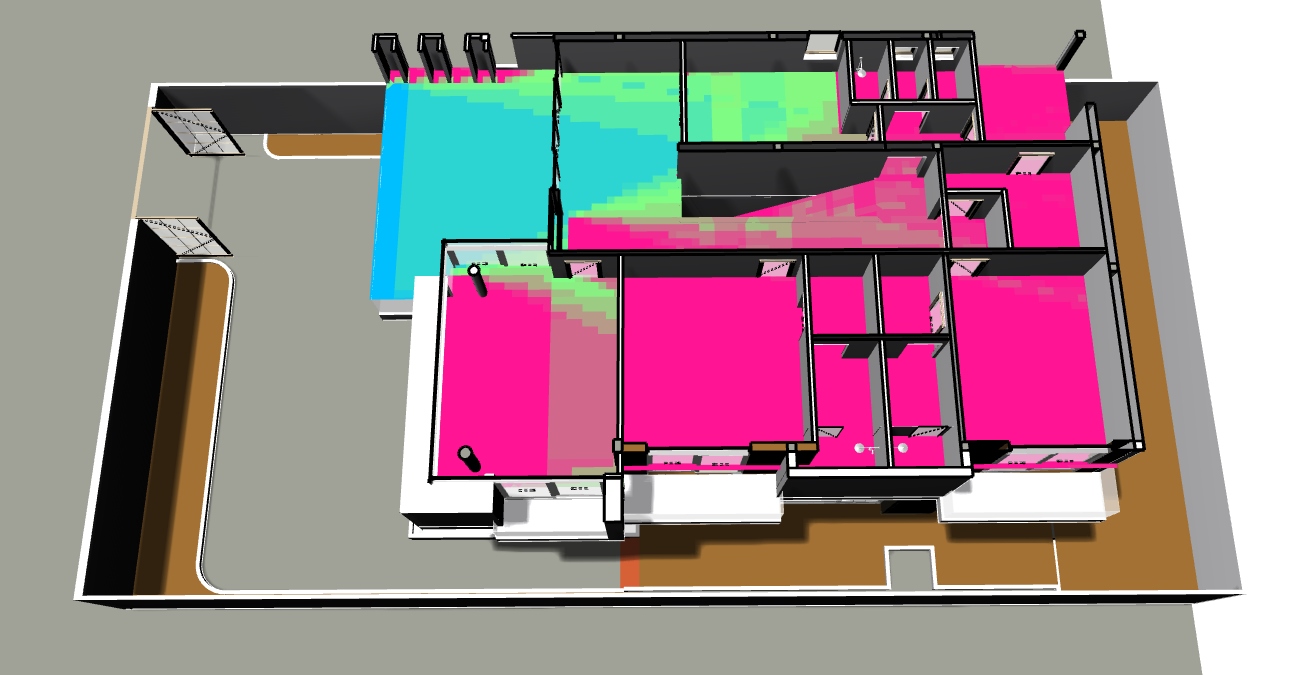
Heating/Cooling Load :
This work calculates the heating and cooling loads for the zone.
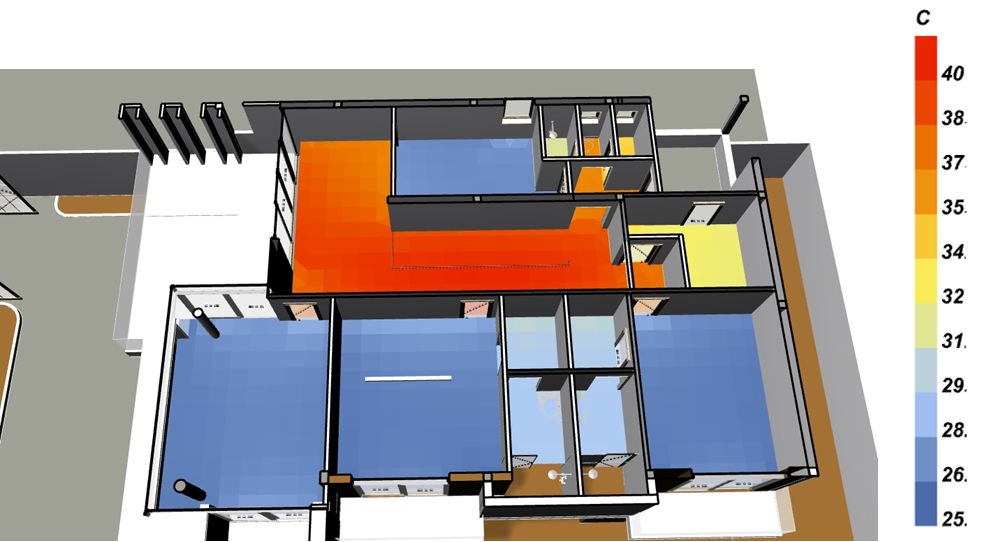
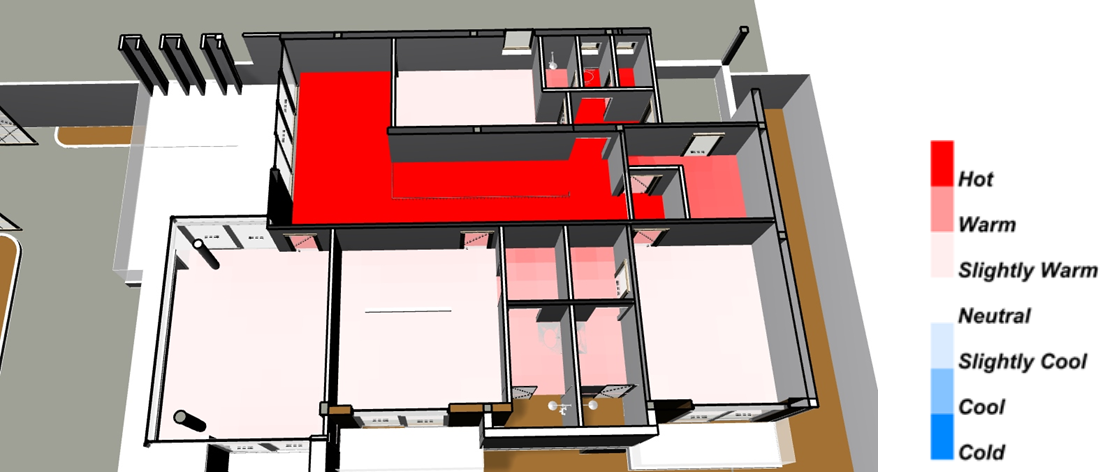
Thermal Comfort :
This work calculates distributions of Predicted Mean Vote and Mean Radiant Temperature across the floor area.

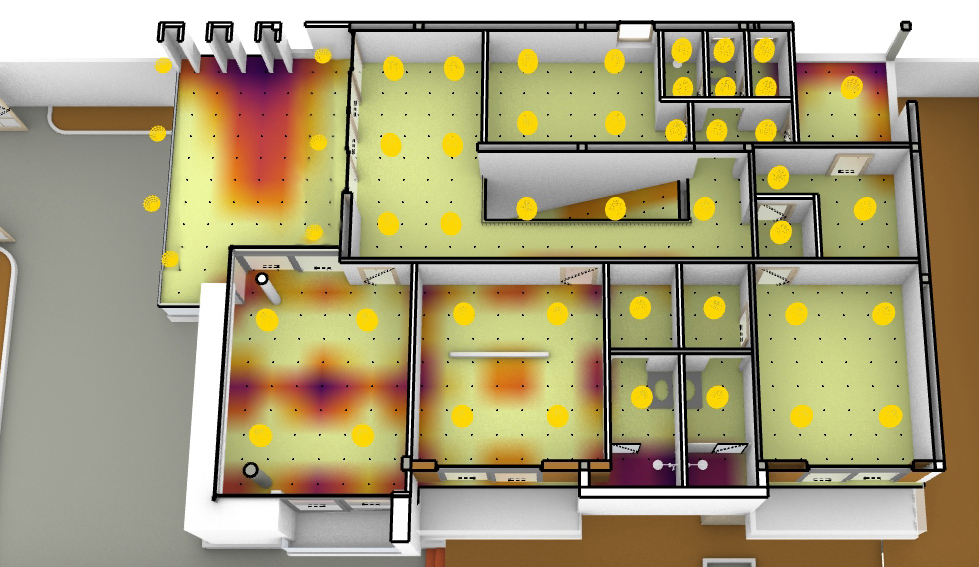
Electric lighting :
This work calculates illuminance distributions for electric lighting.
Acoustic Simulation :
This work helps to predict noise, visualize sound propagation, and critically listen to designed spaces.
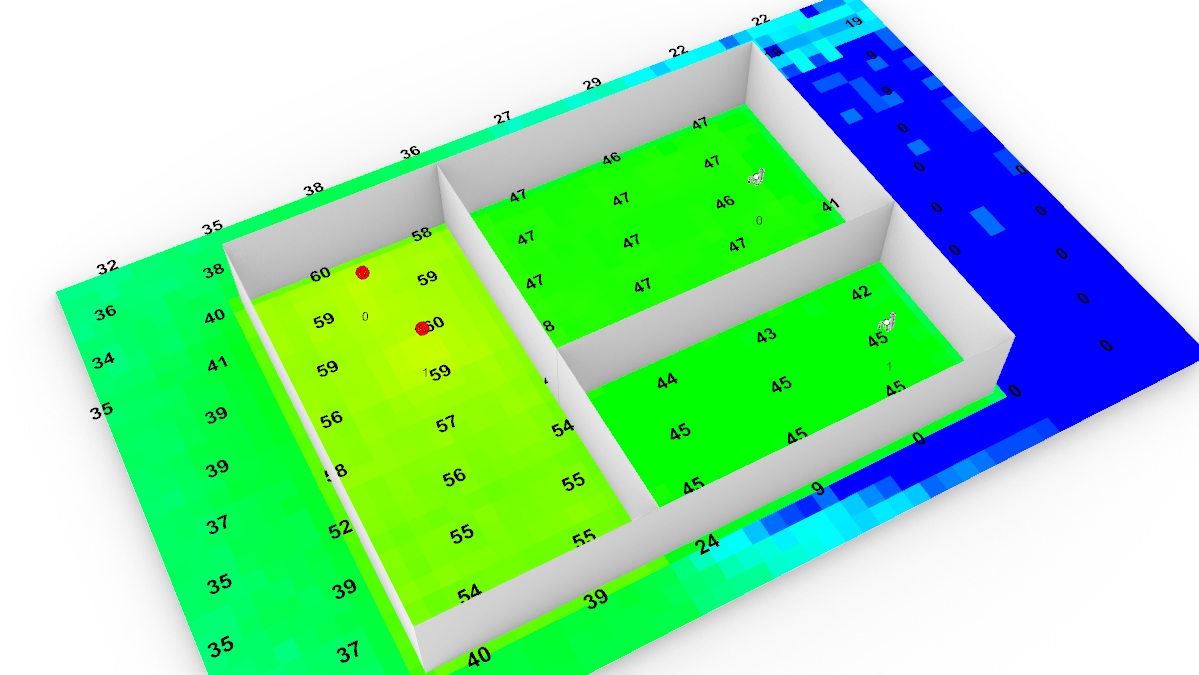
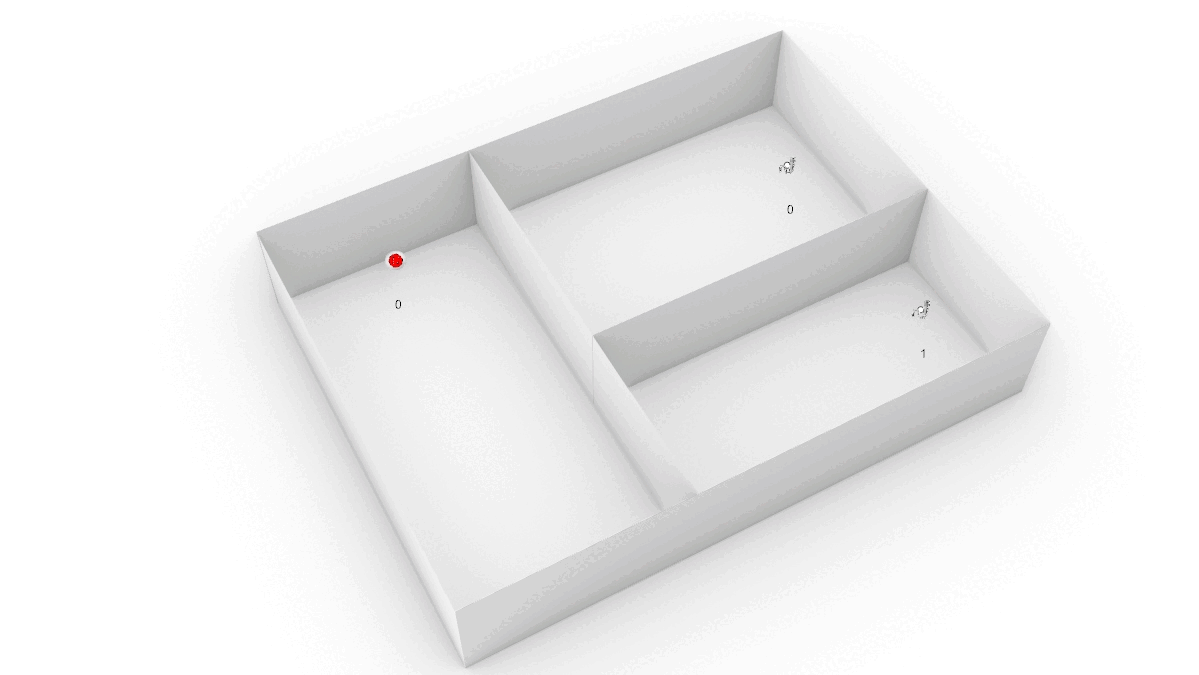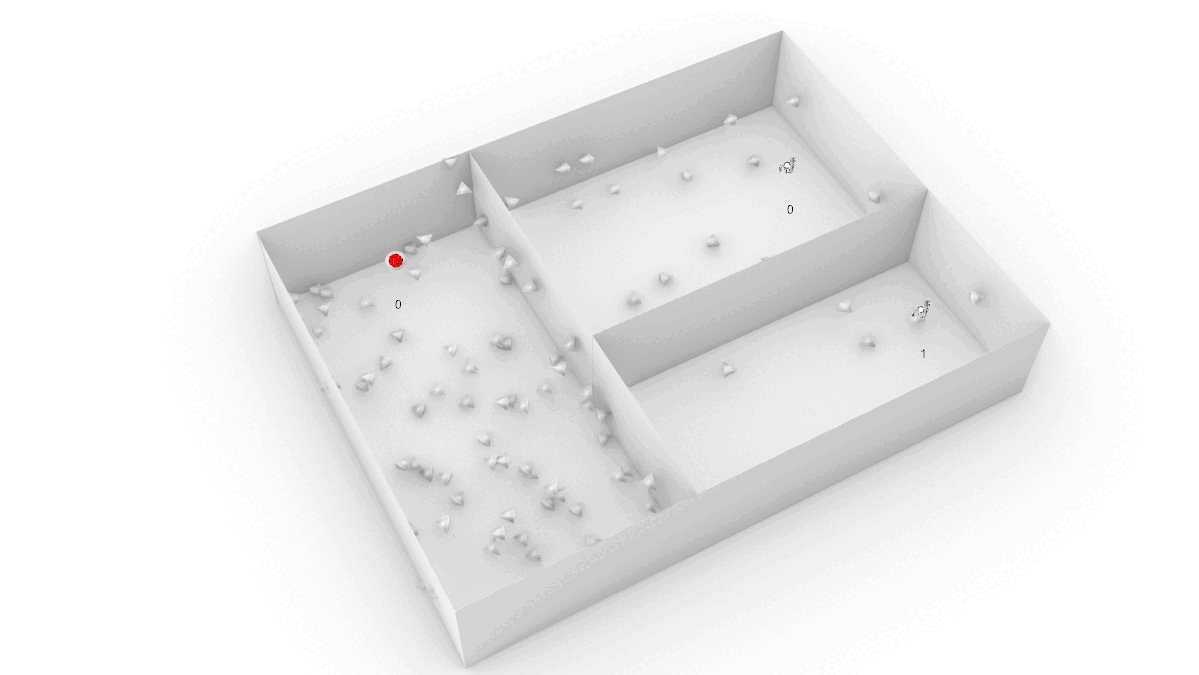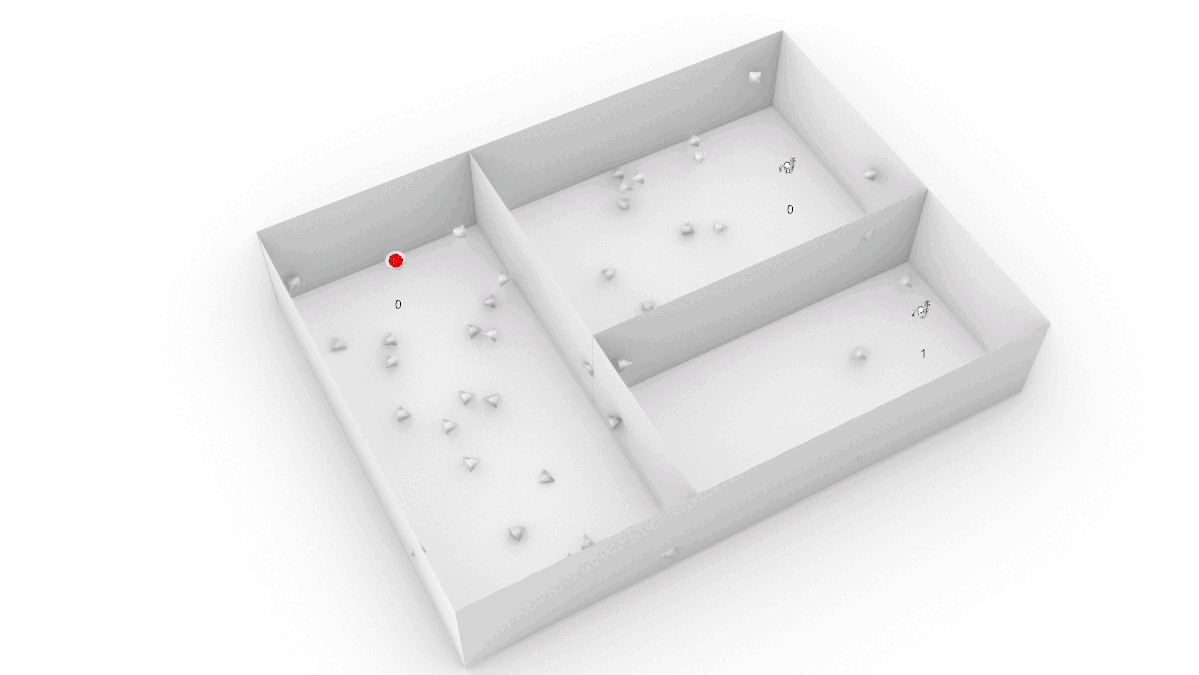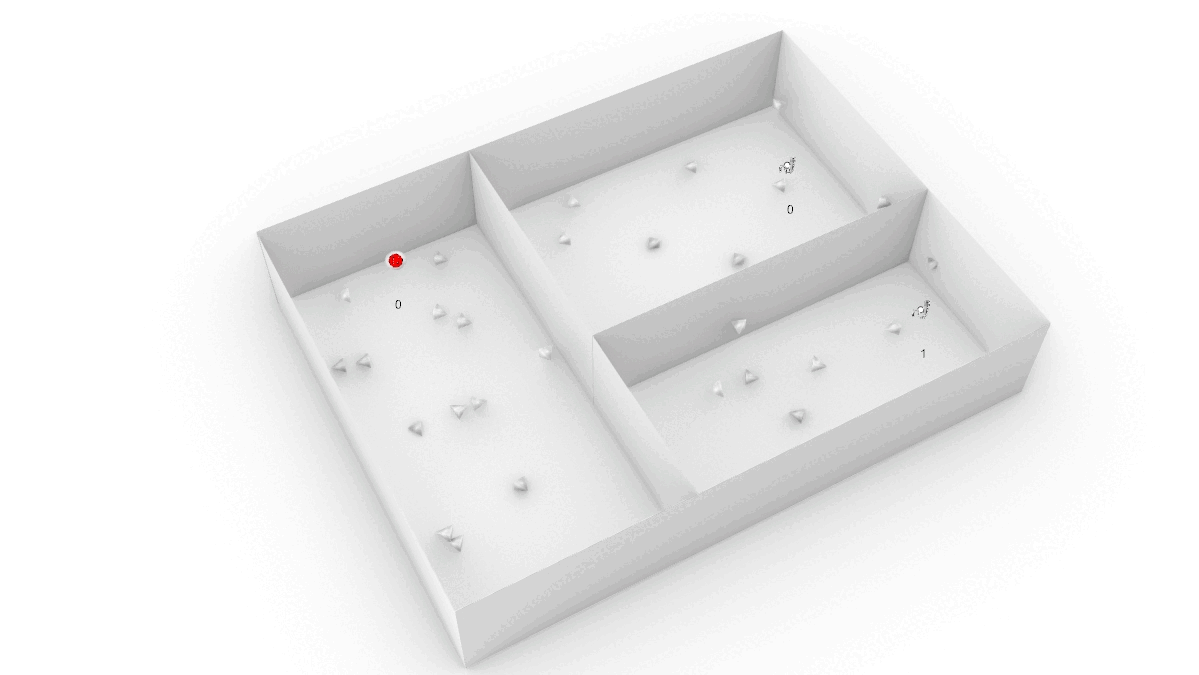
Optimizing Airflow :
Analyze airflow and optimize the ventilation system to achieve design goals (comfort temperature, flow rate, velocity, etc.)
 |
Velocity (m/s) |
Temperature (degC)
|
Fire & Evacuation Simulation :
Simulation of the building's evacuation capability combined with the simulation results of FDS fire and smoke control.
タグ
関連ニュース
HVACにおけるCFD:技術ツールか、それとも単なる可視化か?
CFDは次のような目的で使われているだけだ、と思われがちです。・レポート用のカラフルな画像作成・施主に分かりやすく説明するためのイメージ図 しかし、正しく使用されたCFDは、HVAC運用リスクを低減するための重要な技術ツールです。 CFDで早期に発見できる課題 CFDは、従来の計算手法では見逃されがちなリスクを可視化します。・外気がショートサーキットし、居住域に届いていない・風速が高く、不快なドラフトが発生・室内温度分布の不均一・空間形状に適さない吹出口・吸込口の配置 「本来のCFD解析」に必要な要素とは 適切なCFD解析には、以下が不可欠です。・明確な評価基準との整合(ASHRAE 55、ASHRAE 62.1)・評価対象を居住域(Occupied Zone)に集中・単なる可視化に留まらず、規格適合性に関する結論を提示 SAOでは、CFDを単なる説明用ツールではなく、技術的な検証手法として活用しています。 👉 ASHRAE基準に基づくSAOのCFDアプローチをご紹介します。...
詳細を見る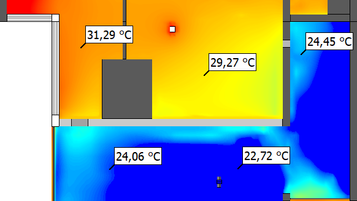
計算上は問題ない HVAC なのに、なぜ不快感が生じるのか?
多くのオフィス、ホテル、商業施設プロジェクトにおいて、HVAC システムは計算上の能力および風量に基づいて適切に設計されています。しかし、実際に運用を開始すると、利用者から以下のような不満が頻繁に寄せられます。 あるエリアは寒すぎる一方、別のエリアは暑い 直吹きの気流による不快感 期待される快適性が得られない執務・滞在空間 これらの問題の原因は、設備能力ではなく、空間内における空気の分布方法にあるケースがほとんどです。 計算結果 ≠ 実際の体感 従来の設計計算では、以下を満たすことができます。 総風量 空間全体の熱負荷 しかし、次の点までは把握できません。 室内における気流の流れ方 デッドゾーンやショートサーキット現象の発生 人が滞在する occupied zone における実際の環境条件 CFD...
詳細を見る
空気の質:基準は枝葉、環境こそが根本である
現在の資料、特にIAQに関するホワイトペーパーを見ると、ひとつの明確な事実が浮かび上がる。世界共通の統一された室内空気質(IAQ)基準は、いまだ存在していない。各国・各組織でガイドラインや基準が大きく異なり、その結果、政府、システムインテグレーター、建築主、そして一般社会は、明確で行動可能な指標を持てずにいる。 しかし、より本質的な問いは「基準が不足していること」ではない。なぜ私たちは、空気を“守る”ために、これほど多くの基準や装置に依存するようになったのか。 問題の根本は、室内空間ではなく、人類の自然環境そのものにある。資源を過剰に消費し、必要以上にエネルギーと物質を使い続けることで、自然環境は破壊され、屋外の空気が汚染される。その結果として、室内空気質の悪化が避けられなくなる。そして私たちは、その“結果”に対処するため、さらに多くの基準、機器、システムを生み出すことになる。 別の視点から見れば、現在のIAQ基準やソリューションの一部は、商業的目的と強く結びついていることも否定できない。センサー、空気清浄機、高度なHVAC機器の大量生産は、資源、エネルギー、そして製品ライフサイクル全体での環境負荷を伴う。慎重に扱わなければ、「健康を守るための技術」が、結果的に環境破壊を助長するという矛盾を生む可能性がある。 もちろん、IAQ基準そのものが誤りというわけではない。特に弱い立場の人々を守り、社会の認識を高めるために、基準は必要である。しかし、基準はあくまで手段であり、目的ではない。 真の目的は、自然と調和した暮らし方に立ち返ることだ。足るを知り、不要な消費を減らし、資源を尊重し、自然換気、緑化、持続可能な設計を優先する。環境が守られていれば、空気の清浄さは管理対象ではなく、当たり前の前提となる。 結局のところ、環境を愛することは、センサーや基準から始まるのではない。それは一人ひとりの意識と選択から始まる。環境が守られたとき、空気の質は技術競争の対象ではなく、**「お金で買うものではない、自然からの贈り物」**として本来の姿を取り戻すだろう。...
詳細を見る





