What is ASHRAE Standard 241?
ASHRAE Standard 241, Control of Infectious Aerosols, is a new standard designed to minimize the spread of airborne infectious diseases in buildings. Based on the latest research and expertise, the standard provides requirements for various aspects of air systems, including design, installation, operation, and maintenance.
In simple terms, Standard 241:
- Sets minimum clean air requirements to reduce the risk of airborne disease transmission in commercial and residential buildings.
- Requires buildings to implement additional measures to control the spread of infectious aerosols during periods of high risk, such as flu season.
- Encourages the use of filtration and air cleaning technologies to improve indoor air quality.
Prerequisites:
Before applying Standard 241, buildings must meet the ventilation and indoor air quality (IAQ) requirements specified in ASHRAE 62.1.
Key aspects of ASHRAE Standard 241:
- Infection Risk Management (IRMM) Regime: Identifies additional layers of engineering controls to be implemented during periods of high transmission risk.
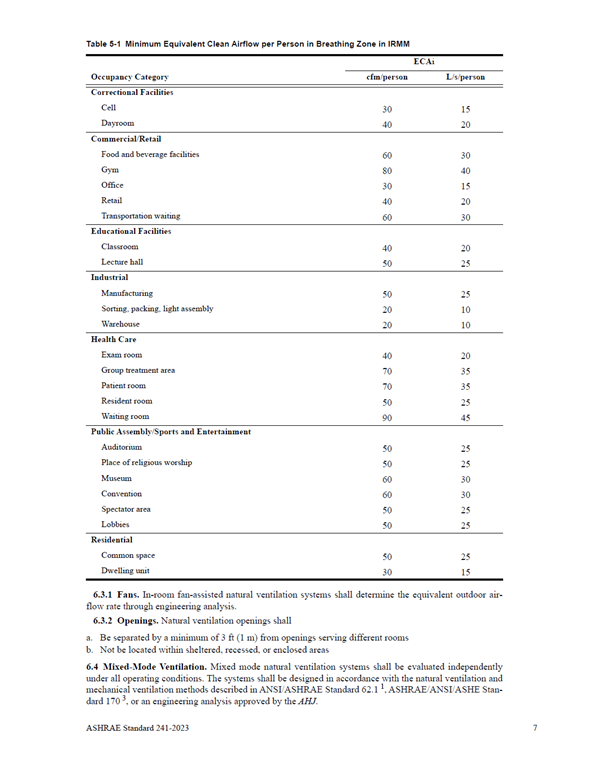
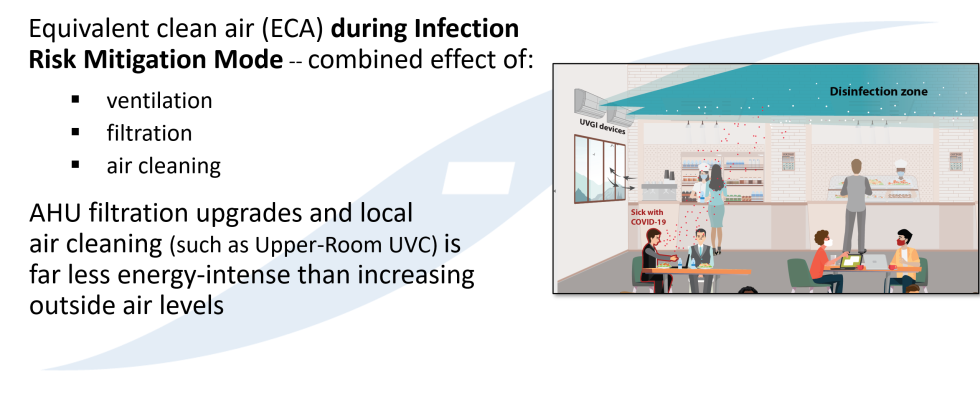
- Equivalent Clean Airflow Rate (ECAi) Requirements: Focuses on filtration, cleaning, and disinfection of air to control indoor air quality.
- Use of Filtration and Air Cleaning Technologies: Encourages the use of engineering controls to achieve the desired equivalent air changes.
- Planning and Operation: Requires assessments and planning to develop a building readiness plan, as well as outlines system operation procedures to ensure effectiveness.
Benefits of adopting ASHRAE Standard 241:
- Reduces the risk of airborne disease transmission.
- Improves indoor air quality and occupant health.
- Saves energy and reduces carbon emissions.
In summary:
ASHRAE Standard 241 is a critical tool for minimizing the spread of airborne infectious diseases in buildings. Buildings should adopt this standard to protect occupant health and improve indoor air quality.
For more information:
Tags






