Did you know that indoor air quality can be 2-5 times worse than outdoor air? 😮 This can have serious impacts on our health and productivity. Luckily, an efficient ventilation system can solve this problem! However, evaluating and optimizing a building's ventilation system is not a simple task. How do you know if your current ventilation system is working well? How can you improve it? And is natural or mechanical ventilation the best choice? In this article, we will guide you on how to evaluate both natural and mechanical ventilation systems and provide practical solutions to improve ventilation efficiency in your building. From an overview of ventilation systems to methods of combining natural and mechanical ventilation, this article will provide you with all the necessary information to create a healthier living and working environment. Let's explore! 💨🏢

Overview of Building Ventilation Systems
Ventilation: Why It Matters
Ventilation is the process of exchanging air within a confined space with the outdoor air. The primary purposes of ventilation are to:
- Remove pollutants and odors
- Provide fresh air
- Regulate temperature and humidity
- Control the concentration of contaminants
Ventilation plays a crucial role in health and productivity:
| Health Benefits | Performance Benefits |
| Reduces the risk of respiratory diseases | Increases focus and concentration |
| Inhibits the growth of mold | Reduces fatigue and headaches |
| Removes allergens | Improves work productivity |
| Improves sleep quality | Creates a comfortable working environment |
Distinguishes between natural and mechanical ventilation
- Natural ventilation:
- Utilizes natural forces like wind and temperature differences
- Requires no mechanical equipment
- Energy-efficient but difficult to control
- Mechanical ventilation:
- Uses fans and ducts to circulate air
- Can be precisely controlled
- Consumes energy but is more effective at filtering air
The selection of a suitable ventilation system depends on various factors such as building type, climatic conditions, and specific usage requirements.

Evaluating Natural Ventilation Systems
A. Identifying Weaknesses and Limitations:
When assessing natural ventilation systems, identifying weaknesses and limitations is a crucial first step. Common issues to look out for include:
- Inappropriate window placement
- Insufficient window size
- Lack of roof vents
- Unfavorable wind direction
B. Monitoring Indoor Air Quality:
Monitoring indoor air quality helps gauge the effectiveness of a natural ventilation system. Key indicators to track include:
| Indicator | Safe Level |
| CO2 | < 1000 ppm |
| Humidity | 30-60% |
| Temperature | 20-26°C |
| PM2.5 | < 35 μg/m³ |
C. Methods for Assessing Airflow
There are several methods to assess airflow in natural ventilation systems:
- Anemometer: A device used to measure wind speed.
- Smoke test: A visual method to observe airflow patterns.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): A computer simulation method to model fluid flow.
- CO2 concentration measurement: Measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide to infer ventilation rates.
D. Factors Affecting Natural Ventilation Performance
The effectiveness of natural ventilation depends on various factors:
- Outdoor climatic conditions: Weather conditions such as wind speed and direction.
- Building design and construction: The layout, orientation, and materials of the building.
- Wind direction and speed: The prevailing wind direction and its strength.
- Temperature difference: The difference in temperature between the indoor and outdoor environments.
- Surrounding obstacles: Buildings or structures that can obstruct airflow.
Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing natural ventilation systems, ensuring good indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Next, we will explore how to evaluate mechanical ventilation systems for a comprehensive view of building ventilation.

Evaluating Mechanical Ventilation Systems
After examining natural ventilation systems, let's now focus on evaluating mechanical ventilation systems. This is a crucial step in ensuring the efficiency and safety of a building.
Energy Efficiency:
Energy efficiency is a primary consideration when evaluating mechanical ventilation systems. Key aspects to consider include:
- Energy consumption of the system
- Potential for heat recovery from exhaust air
- Efficiency of heat exchangers
Noise and Vibration:
Noise and vibration can impact occupant comfort. Evaluation should include:
- Noise levels in different areas of the building
- Vibration of ductwork and equipment
- Effectiveness of soundproofing and vibration dampening measures
Ductwork and Filters:
Ductwork and filters play a crucial role in distributing and cleaning the air. Inspection should cover:
- Condition and airtightness of ductwork
- Filter efficiency
- Maintenance and replacement frequency of filters
Fan and Motor Performance:
Fans and motors are the heart of a mechanical ventilation system. Evaluation should include:
| Criteria | Description |
| Capacity | Ensuring it meets ventilation requirements |
| Efficiency | Checking energy consumption |
| Lifespan | Determining when maintenance or replacement is needed |
By conducting a thorough evaluation of a mechanical ventilation system, we can identify its strengths and weaknesses and implement appropriate improvements.

Improving Natural Ventilation
After assessing the current natural ventilation system, we will now explore methods to enhance natural ventilation within buildings. One effective approach is to optimize window placement and size.
Proper window placement is crucial for maximizing natural ventilation. Key considerations include:
-
Placing windows to capture prevailing winds
-
Ensuring windows account for 20-25% of the floor area
-
Using operable windows to control airflow
Additionally, incorporating green building design elements can enhance natural ventilation:
-
Creating rooftop gardens to increase airflow
-
Designing courtyards to create stack effect
-
Using green walls or vertical gardens to filter air
Cross ventilation is another effective method to induce airflow:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Increases wind speed | Relies on outdoor wind conditions |
| Reduces indoor temperature | Can cause noise during strong winds |
| Saves energy | May be difficult to control in extreme weather |
The stack effect leverages temperature and pressure differences to create airflow:
- Create vertical spaces
- Place windows high to allow hot air to escape
- Provide voids between floors for air circulation
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve natural ventilation in your building. Next, we will explore methods to upgrade mechanical ventilation systems to optimize indoor air quality.

Upgrading Mechanical Ventilation Systems
After evaluating existing mechanical ventilation systems, let's delve into methods for improving their performance and efficiency.
A. Implementing Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV): HRV systems are highly efficient solutions for saving energy. They operate by:
-
Recovering heat from the exhaust air
-
Transferring this heat to incoming fresh air
-
Reducing the load on the HVAC system
-
Improving indoor air quality
Comparison of HRV:
| Criteria | Without HRV | With HRV |
| Energy efficiency | Low | High |
| Operating cost | High | Low |
| Air quality | Moderate | Excellent |
B. Integrating Intelligent Control Systems: Integrating various sensors and control systems can optimize the operation of mechanical ventilation systems:
- Monitoring CO2 levels and air quality
- Automatically adjusting fan speed based on occupancy and demand
- Creating intelligent schedules based on building usage
C. Enhancing Ductwork and Filtration: To improve overall system performance, consider:
- Inspecting and sealing ductwork to prevent leaks
- Upgrading filters to high-efficiency options like HEPA or activated carbon
- Optimizing ductwork design to reduce resistance and increase airflow
D. Installing High-Efficiency Fans and Motors: Replacing old fans and motors with high-efficiency models offers several benefits:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Improved airflow control
- Lower noise levels and extended lifespan
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of your mechanical ventilation system.
Next, we will explore how to combine natural and mechanical ventilation systems to create an optimal ventilation solution for your building.
Combining Natural and Mechanical Ventilation
Combining natural and mechanical ventilation is an optimal strategy for creating ideal indoor air conditions. This approach harnesses the best of both worlds, resulting in numerous benefits.
Optimizing Indoor Comfort and Air Quality
By integrating both natural and mechanical ventilation systems, we can:
-
Maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels
-
Effectively remove pollutants, odors, and unwanted substances
-
Create a natural, pleasant airflow
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
Leveraging natural ventilation when conditions permit and switching to mechanical ventilation when necessary can significantly:
-
Reduce energy consumption
-
Lower operating costs
-
Minimize environmental impact
Intelligent System Integration
A sophisticated control system can:
-
Monitor indoor and outdoor environmental conditions
-
Automatically switch between natural and mechanical ventilation modes
-
Optimize system performance based on real-time data
Designing a Comprehensive Combined Ventilation System
A well-designed combined ventilation system should include:
| Element | Description |
| Window placement | Optimized for natural ventilation |
| Ductwork system | Designed for flexibility in both natural and mechanical modes |
| Sensors |
Measure air quality and environmental conditions |
| Control system | Incorporates AI for efficient management |
By intelligently combining natural and mechanical ventilation, buildings can achieve optimal indoor air quality, reduce energy consumption, and enhance occupant comfort.

Evaluating and improving a building's ventilation system is crucial for ensuring a comfortable and healthy living or working environment. By analyzing both natural and mechanical ventilation systems, we can identify their strengths and weaknesses and develop tailored solutions. Ultimately, a harmonious integration of natural and mechanical ventilation will yield optimal results. Regular assessment and improvement of ventilation systems ensure the best possible indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption and operating costs.
Tags
Related news
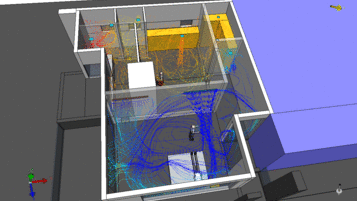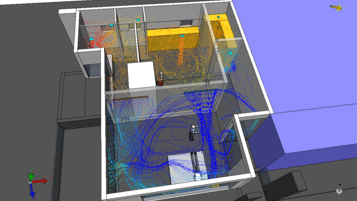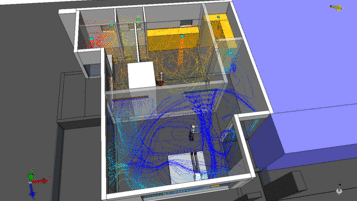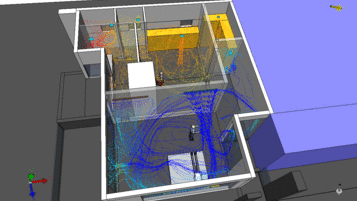
CFD in HVAC: Engineering Tool or Just Visualization?
Many people believe that CFD is used only to: Create colorful images for reports Provide visual illustrations for clients In...
View detail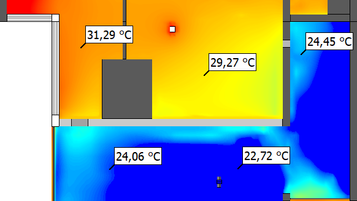
Why do occupants still feel uncomfortable even when the HVAC system is correctly designed?
In many office, hotel, and commercial projects, HVAC systems are designed strictly according to calculated capacity and airflow. However, once...
View detail
Air Quality: Standards Are the Branches, the Environment Is the Root
According to current documents, including IAQ white papers, one clear reality emerges:there is still no unified global standard for indoor...
View detail





